Blog
ITC Monthly Wrap-Up: April 2022
This month’s ITC wrap up reviews one decision from April and one from March, which highlight: (1) how the ITC handles exclusion orders as marketplaces move online; and (2) the impact of Federal Circuit remands at the ITC, as well as the availability of advisory opinions from the ITC.
Certain In Vitro Fertilization Products, Components Thereof, and Products Containing the Same (Inv. No. 337-TA-1196)
The first case deals with the Commission's issuance of a limited exclusion order and cease-and-desist order in Certain In Vitro Fertilization Products, Components Thereof, and Products Containing the Same (Inv. No. 337-TA-1196).
In March of 2020, Complainant Merck KGaA affiliate EMD Serono, Inc. of Rockland, Massachusetts ("EMD") alleged violations of Section 337 by Respondent FastIVF of Scottsdale, Arizona ("FastIVF"), et. al. Complaint, at 1. EMD alleged that FastIVF was importing and selling unlawful in vitro fertilization ("IVF") products that infringe eight U.S. Trademark Registrations.[1] EMD alleged that the products sold and imported by FastIVF were unauthorized versions of Gonal-f, Ovidrel, and OvitrelleâEMD's fertility drugs. Respondents' drugs were sold through "semi-anonymous internet pharmacies."
Importantly, FastIVF defaulted and the 1196 Investigation was terminated against the remaining Respondent based on Complainant's withdrawal of the complaint. However, in its complaint, EMD requested that the Commission issue a GEO. In the subsequently issued ID, Judge Bullock explained that a GEO was an appropriate remedy because the Respondents' fertility drugs were sold through "semi-anonymous internet pharmacies" that could easily circumvent a Limited Exclusion Order ("LEO"). On October 6, 2021, the Commission remanded the investigation and vacated the ID in part with respect to the finding that the economic prong of the domestic industry requirement had been satisfied.
On remand, EMD withdrew its request for a GEO and sought instead a LEO against the defaulting Respondents and a cease-and-desist order against FastIVF, which it got in Judge Bullock's December 2021 ruling finding a violation of Section 337. Shortly thereafter, the Commission affirmed the FID and requested briefing on remedy, public interest, and bonding. After reviewing the briefing on the issues, the Commission determined that the appropriate remedy was an LEO directed to the defaulting Respondents, and a CDO directed to FastIVF.
This decision is interesting because it demonstrates the impact of the online marketplace on the scope of potential remedies.
Certain Foam Footwear (Inv. No. 337-TA-567)
The next decision is an advisory opinion from the Commission, which issued on March 28, 2022 in Certain Foam Footwear (Inv. No. 337-TA-567).
There, the ITC found third party Triple T Trading Limited’s (“Triple T”) Northside Classic Fur Lined Clog with permanent fleece liming and its Northside Clog (together, “Two Footwear Models”) with permanent plastic washers did not infringe U.S. Patent No. 6,993,858 ("the '858 patent) and, therefore, did not fall within the scope of the GEO issued in the investigation. The ITC also determined that, because the claims of U.S. Patent No. D517,789 expired on March 28, 2020, the only patent remaining at issue is the '858 patent.
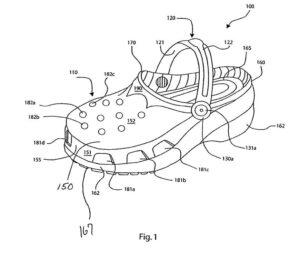
'858 Patent, Fig. 1.
The 567 Investigation was originally instituted in 2006 based on a complaint filed by Crocs, Inc. (“Crocs”) alleging violation of Section 337 in the importation and sale of foam footwear. Complaint at 1—2. In July 2008, the Commission issued a final determination finding no violation. The decision was subsequently appealed to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit. On February 24, 2010, the Court remanded the finding and vacated the Commission’s prior finding of no violation. Crocs, Inc. v. Int’l Trade Comm'n, 598 F.3d 1294, 1297 (Fed. Cir. 2010).
After the case was remanded and vacated, the Commission determined that there was a violation of Section 337 and issued a cease-and-desist letter. In November of 2021, Triple T sought institution of an advisory opinion to determine whether its Two Footwear Models fall within the scope of the GEO. The Commission issued the requested advisory proceeding on December 17, 2021, and on March 28, 2022, determined there was no infringement aligning their findings with the Federal Circuit's remand.
Unlike Federal Courts, which are precluded from issuing advisory opinions under Article III of the U.S. Constitution, the ITC is allowed to issue advisory opinions. An advisory opinion provides non-binding guidance with respect to the legal implications of a situation that is not the subject of an actual case or controversy. Pursuant to 19 C.F.R. § 210.79, the ITC is authorized to issue advisory opinions to determine whether certain conduct—e.g., the importation of a redesigned or new productâwould violate an existing exclusion, cease-and-desist, or consent order.
[1] The eight U.S. Trademark Registration Numbers are 4,689,651; 1,772,761; 3,777,170; 3,389,332; 3,816,320; 1,972,079; 3,604,207; and 3,185,427.
The opinions expressed are those of the authors on the date noted above and do not necessarily reflect the views of Fish & Richardson P.C., any other of its lawyers, its clients, or any of its or their respective affiliates. This post is for general information purposes only and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal advice. No attorney-client relationship is formed.